What skills do young children need to thrive in life? How do we know if a child is developing “normally”? Are we giving them the proper support in the right areas, or only focusing on surface-level learning? Even experienced educators may overlook critical aspects of a child’s growth without a clear understanding of developmental domains.
The five core developmental domains include physical, cognitive, language, social-emotional, and adaptive. These developmental domains reflect how children grow, learn, interact, and adapt to the world around them. Understanding these areas is essential for designing 적절한 학습 환경 그리고 각 어린이가 자신의 잠재력을 최대한 발휘하도록 보장합니다.
Each developmental domain works in harmony with the others, shaping the whole child. This article will explore how they interact and why they matter deeply in early education settings.

발달 영역은 무엇인가?
Developmental domains are the distinct areas where children grow and acquire skills from birth through early childhood. These areas represent the key components of human development. They help educators, caregivers, and developmental specialists observe, guide, and assess a child’s progress. The term domains of development refers specifically to how these areas are categorized and studied in child development theory.
널리 알려진 발달 영역은 5가지가 있습니다.
- 신체 발달 – 신체, 근육, 운동 조정, 감각 인식의 성장이 포함됩니다.
- 인지 발달 – 사고 능력, 기억력, 추론 능력, 문제 해결 능력을 포함합니다.
- 언어 발달 – Includes receptive (understanding) and expressive (speaking or communicating) language skills.
- 사회정서적 발달 – 어린이가 감정을 이해하고, 관계를 형성하고, 행동을 조절하는 방법과 관련이 있습니다.
- 적응형 개발 – 옷 입기, 식사하기, 일상 생활 따르기, 개인적 책임감과 같은 실용적인 생활 기술을 말합니다.
이러한 각 발달 영역은 필수적이고 서로 연관되어 있지만, 각 영역마다 고유한 초점과 관찰 가능한 이정표가 있습니다. 전문가들은 이러한 범주를 활용하여 아동의 발달 과정을 모니터링하고 아동이 나이에 비해 정상적으로 발달하고 있는지 확인합니다.
간단히 말해, 발달 영역은 어린이가 서로 다르지만 연결된 영역에서 어떻게 성장하는지 이해하는 틀 역할을 하며, 유아 교육에 대한 체계적이고 포괄적인 접근 방식을 가능하게 합니다.
발달 영역이 중요한 이유는 무엇인가?
발달 영역의 중요성을 이해하는 것은 유아 교육에 참여하는 모든 사람에게 매우 중요합니다. 이러한 영역은 우리가 아이들의 성장을 관찰하고, 지원하고, 이끌어가는 렌즈 역할을 합니다. 각 영역을 개별적으로 고려하고 서로 어떻게 연결되는지 살펴볼 때, 우리는 더 나은 교육적 결정을 내리고 더욱 의미 있는 학습 경험을 제공할 수 있습니다.
성장을 이해하기 위한 프레임워크
The concept of developmental domains provides a systematic way to understand child development. Rather than viewing growth as a general or abstract idea, the domains of development organize progress into observable categories: physical, cognitive, language, social-emotional, and adaptive. This framework helps professionals identify strengths, target support, and track milestones more clearly.
전인교육 지원
아이들은 단순히 읽고 셈하는 법을 배우는 것이 아니라, 움직이고, 타인과 관계를 맺고, 자신을 돌보는 법도 배웁니다. 모든 아이는 학업적인 면뿐 아니라 다섯 가지 발달 영역 전반에서 발달합니다. 균형 잡힌 접근 방식은 신체 활동, 정서적 웰빙, 의사소통, 그리고 생활 기술이 일상생활에 자연스럽게 스며들도록 합니다. 이를 통해 아이들은 더욱 자신감 있고, 유능하며, 회복탄력적인 학습자로 성장합니다.
지연의 조기 식별
When educators and caregivers understand the domains of development, they are more equipped to spot early warning signs. If a child is not speaking as expected or struggling with coordination, these observations can be linked to the appropriate developmental domain. Early identification enables timely intervention, significantly improving long-term outcomes and reducing delays’ impact.
커리큘럼 및 환경 디자인 지도
High-quality educational environments are intentionally designed around developmental domains. This affects everything—from selecting age-appropriate materials to structuring daily schedules and physical spaces. When we understand which domain a task supports, we can ensure that every part of the learning environment contributes to the child’s growth in a targeted and meaningful way.
개별 학습 촉진
Each child progresses differently across the developmental domains. One child may excel in language but need more support with social-emotional regulation. Another may be physically confident but needs help with fine motor control. Recognizing these differences allows educators to tailor strategies, differentiate instruction, and create inclusive, responsive learning plans that meet individual needs.
학습에 영감을 주는 공간을 디자인할 준비가 되셨나요? 교실의 필요에 맞춘 맞춤형 가구 솔루션을 위해 저희에게 문의하세요.
신체적 발달 영역
다섯 가지 발달 영역 중 신체 발달 영역은 유아기에 가장 눈에 띄고 측정하기 쉽습니다. 신체 발달 영역은 아동의 신체 성장, 조절 능력, 근력, 그리고 협응력의 발달 과정을 나타냅니다. 이 영역에는 달리기나 점프와 같은 대근육 운동 능력부터 연필 잡기나 신발끈 묶기와 같은 소근육 운동 능력까지 모든 것이 포함됩니다. 신체 발달 영역의 건강한 발달은 아동이 주변 환경을 탐험하고, 그룹 활동에 참여하며, 신체 능력에 대한 자신감을 키울 수 있도록 해줍니다.

신체 발달의 핵심 구성 요소
대근육 운동 기술
Gross motor skills involve large muscle groups for walking, running, jumping, balancing, and climbing. These are usually the first to develop and are essential for overall mobility and participation in outdoor activities. Children develop these skills through free play, structured physical education, and daily movement routines.
미세 운동 기술
Fine motor skills refer to smaller, precise movements of the hands and fingers. These include drawing, cutting with scissors, buttoning clothes, and building with small blocks. Mastery of these skills supports school readiness, especially in writing, arts and crafts, and independent dressing.
감각 및 공간 인식
아이들은 또한 자신의 몸이 공간 어디에 있는지, 그리고 감각 정보를 어떻게 처리하는지에 대한 내적 이해를 발달시켜야 합니다. 여기에는 촉각 민감도, 시각-운동 협응력, 그리고 균형 감각이 포함됩니다. 이 영역에 문제가 있으면 주의력, 행동, 또는 과제 완수에 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
연령별 신체 발달 이정표
일반적인 신체 발달 이정표를 이해하면 교육자와 보호자가 아이의 성장이 예상 패턴과 일치하는지 파악하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 개인차는 자연스러운 현상이지만, 명확한 기준은 발달 영역의 진행 상황을 관찰하는 데 유용한 지침을 제공합니다.
| 연령대 | 대근육 운동 발달 이정표 | 미세 운동 발달 이정표 |
|---|---|---|
| 0~12개월 | 머리를 들어올리고, 뒤집히고, 지지대 없이 앉고, 기어다닙니다. | 물건을 잡으려고 손을 뻗고, 물건을 손으로 옮기고, 손가락으로 긁는다. |
| 1~2년 | 2~4개의 블록을 쌓고, 숟가락을 사용하고, 크레용으로 낙서합니다. | 몇 글자를 쓰고, 작은 도구를 사용하여 통제하고, 신발끈을 묶습니다. |
| 2~3년 | 2~4개의 블록을 쌓고, 숟가락을 사용하고, 크레용으로 낙서합니다. | 달리고, 두 발로 점프하고, 공을 차기 시작합니다. |
| 3~4년 | 독립적으로 걷고, 기어오르기 시작하고, 공을 던집니다. | 가위로 자르고, 모양을 그리며, 큰 단추를 끼웁니다. |
| 5~6년 | 페달 삼륜차, 한 발로 잠깐 균형을 잡고 공을 잡습니다. | 페이지를 넘기고 큰 구슬을 묶고 옷의 지퍼를 풀기 시작합니다. |
These milestones reflect how domains of development evolve in tandem. For instance, mastering balance and coordination supports physical competence and boosts a child’s self-confidence and participation in group settings, highlighting the interconnection between physical and social-emotional domains.

유아기 신체 발달을 지원하는 방법
신체 발달 영역은 아동기의 여러 단계에 걸쳐 빠르게 발전합니다. 각 단계의 성장을 지원한다는 것은 발달적으로 적절한 것이 무엇인지 이해하고 적절한 재료, routines, and challenges. Below is a breakdown of enhancing physical growth across various age groups.
유아
유아기에는 코어 근력과 운동 협응력 강화에 중점을 둡니다. 엎드려 자는 시간은 목, 등, 어깨 근육 강화에 필수적이며, 이는 기어 다니고 앉는 데 중요한 기초가 됩니다. 부드러운 매트와 연령에 맞는 장난감을 사용하여 안전한 바닥 공간을 마련하고, 뻗고, 구르고, 잡는 것을 장려하세요. 이 시기의 움직임은 모든 발달 영역, 특히 감각 및 인지적 참여에 있어 초기 발달을 촉진합니다.
유아/2세
Children are learning to walk, climb, and carry objects at this stage. Their gross motor skills proliferate as they begin exploring independently. Offer push toys, soft climbing structures, balls, and pull-along items. Fine motor skills can be supported through stacking blocks, turning pages, and simple self-care, like using spoons. Safe, supervised freedom to move supports both physical growth and confidence, laying a strong foundation in the domains of development.
유치원/유치원
Preschoolers need daily opportunities to run, jump, balance, and manipulate objects. Gross motor skills can be developed through games, tricycles, obstacle courses, and outdoor exploration. Encourage drawing, cutting, lacing, and using small tools for fine motor growth. This age benefits from well-structured environments that balance freedom of movement with guided tasks, ensuring the physical development domain grows alongside cognitive and social-emotional development.
학령기
As children grow older, physical development becomes more refined. Activities that require coordination, strength, and precision are ideal. Team sports, dance, yoga, and structured physical education play a role. Fine motor demands increase, with writing, instrument playing, or crafting becoming central. Promoting regular movement breaks and varied physical challenges keeps children active and supports ongoing progress in the developmental domains.
인지 발달 영역
Cognitive development refers to how children think, learn, explore, and solve problems. It is one of the most central developmental domains because it influences how children understand the world, process information, and apply knowledge. Strong cognitive development is the foundation for academic learning and critical thinking throughout life.

인지 발달의 핵심 구성 요소
주의와 기억
The cognitive development domain’s ability to focus and retain information is a core function. Attention allows a child to engage meaningfully in an activity, while memory enables them to recall prior experiences, which is essential for learning. Activities involving repetition, rhymes, pattern recognition, or storytelling can significantly strengthen these skills from an early age. Simple routines also help build memory by creating predictable sequences that children can anticipate and mentally rehearse.
문제 해결 및 논리적 사고
어린아이들은 사물의 작동 원리를 이해하기 위해 자연스럽게 실험합니다. 블록을 쌓거나, 퍼즐 조각을 돌리거나, 상자를 여는 다양한 방법을 시도할 때, 아이들은 복합적인 사고를 하게 됩니다. 이러한 놀이 행동은 논리력, 추론력, 그리고 인과관계에 대한 이해를 발달시켜 발달 영역을 지원합니다. 아이들이 성장함에 따라 이러한 초기 문제 해결 시도는 사건의 순서를 파악하거나 초기 수학 기술을 사용하는 것과 같은 더 발전된 과제의 기반이 됩니다.
상징적 사고와 상상력적 사고
Pretend play, drawing, storytelling, and using objects as symbols (e.g., a block as a phone) are essential activities in the cognitive development domain. These actions allow children to externalize their internal thinking, develop abstract reasoning, and practice perspective-taking. Symbolic thinking supports early literacy, as children understand that letters and numbers represent meaning. Imaginative activities also support emotional regulation by allowing children to role-play and process their experiences.
분류 및 개념 형성
아이들은 크기, 모양, 색깔, 그리고 용도에 따라 사물을 분류하기 시작합니다. 이를 범주화라고 합니다. 분류하고 짝짓기하는 활동을 통해 아이들은 정신적 개념을 형성하고 유사점과 차이점을 이해하는 능력도 발달합니다. 이러한 능력은 나중에 비판적 사고와 의사 결정의 기초가 됩니다. 인지 발달 영역은 이러한 초기 조작을 활용하여 동물 분류, 반대 개념 이해, 심지어 학령기 과학 개념 이해와 같은 복잡한 과제를 지원합니다.

인지 발달의 이정표: 피아제 4단계
Renowned developmental psychologist Jean Piaget identified four primary stages of cognitive development that explain how children’s thinking evolves. Each stage reflects how children perceive, process, and engage with their environment.
감각운동기(출생~2세)
유아는 감각적 경험과 세상과의 신체적 상호작용을 통해 배웁니다. 이 시기에는 사물이 시야에서 사라져도 여전히 존재한다는 것을 이해하는 대상 영속성이 발달합니다.
전조작기(2~7세)
아이들은 단어나 이미지와 같은 상징을 사용하여 사물을 표현하기 시작합니다. 상상력과 언어는 발달하지만, 사고는 여전히 직관적이고 자기중심적입니다. 아이들은 다른 사람의 관점에서 사물을 보는 데 어려움을 겪습니다.
구체적 조작 단계(7세~11세)
아이들은 논리적 사고를 발달시키지만 여전히 구체적인 개념에 기반을 둡니다. 분류, 서열화, 보존(모양이 변해도 양은 일정하게 유지됨)과 같은 정신적 연산을 수행할 수 있습니다.
공식적 운영 단계(12세 이상)
Abstract reasoning, hypothetical thinking, and deductive logic become possible. Learners can think about moral dilemmas, future planning, and complex problem-solving at this stage.
이러한 단계는 교육자와 가족이 어린이가 인지 발달 영역에서 어느 단계에 있는지 이해하는 데 도움이 되며, 연령에 맞는 기대와 활동을 안내합니다.

유아기 인지 발달을 지원하는 방법
유아
딸랑이와 같은 원인과 결과 장난감을 제공하여 조기 인지를 지원합니다. 부드러운 블록까꿍 놀이, 음악, 그리고 하루 종일 아기와 함께하는 대화는 주의력과 기억력을 강화하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 반복과 예측 가능성은 아기에게 질서 감각을 심어주고 발달 영역의 초기 뇌 발달을 촉진합니다.
유아/2세
이 단계에서 아이들은 시행착오를 통해 탐구합니다. 퍼즐, 쌓기 장난감, 짝 맞추기 게임을 제공합니다. "만약…라면 어떻게 될까요?"와 같은 간단한 질문을 통해 호기심을 북돋아 주세요. 사물의 이름을 말하고 일상 생활에 대해 이야기하는 것은 어휘력을 향상시키고 모든 발달 영역에서 신경 연결을 강화합니다.
유치원/유치원
게임과 이야기를 통해 분류, 패턴화, 숫자 세기, 순서 배열을 소개합니다. 가상 놀이는 추상적 사고력을 향상시킵니다. 블록으로 도시를 짓거나 가게 주인 역할극을 하는 것과 같은 활동은 인지 발달 영역에서 문제 해결 능력과 상징적 사고력을 모두 향상시킵니다.
학령기
Support higher-order thinking with board games, science experiments, and open-ended questions. Give tasks that involve planning and following multi-step instructions. Reading comprehension and storytelling build advanced memory and logic, strengthening the child’s place within all domains of development.
언어 발달 영역
언어는 사고와 의사소통을 연결하는 다리입니다. 언어 발달 영역은 아이들이 자신의 필요, 생각, 감정을 표현하기 위해 언어를 이해하고 사용하는 방식을 다룹니다. 다섯 가지 필수 발달 영역 중 하나인 언어는 인지적 성장, 사회적 상호작용, 그리고 모든 영역의 학습과 깊은 연관이 있습니다.

언어 발달의 핵심 구성 요소
수용 언어
아이들은 말하기 전에 언어를 이해하기 시작합니다. 수용 언어에는 익숙한 단어를 인식하고, 이름에 반응하고, 간단한 지시를 이해하는 것이 포함됩니다. 이러한 능력은 언어 발달 영역에서 의사소통의 기초를 형성합니다.
표현적 언어
Expressive language involves speaking, gesturing, signing, or writing to convey meaning. It starts with cooing and babbling in infancy and grows into complete sentences and storytelling. Expressive skills allow children to share their ideas and needs, making them central to all developmental domains.
어휘 및 단어 사용
Vocabulary growth is one of the most visible aspects of language development. Early words relate to objects and people, but over time, children begin to use descriptive, functional, and emotional language. A rich vocabulary supports academic readiness and reading comprehension.
듣기 및 대화 기술
Actual language development goes beyond vocabulary, including listening, turn-taking, and responding appropriately. These conversational abilities allow children to engage meaningfully in classroom settings and social environments, tying language directly to the domains of development, such as social-emotional growth.
연령별 언어 발달 이정표
언어 발달 영역의 진행 상황을 추적하는 것은 아동의 전반적인 성장을 이해하는 데 매우 중요합니다. 언어 발달 단계는 일반적으로 수용적 영역과 표현적 영역으로 구분되며, 인지 또는 사회정서 발달과 같은 다른 발달 영역의 향상과 연관되는 경우가 많습니다.
| 연령대 | 수용 언어 이정표 | 표현 언어 이정표 |
|---|---|---|
| 0~12개월 | 소리에 반응하고, 이름을 인식하고, "아니요"를 이해합니다. | 옹알이, 중얼거림, 소리 흉내내기, 간단한 몸짓(예: 손 흔들기) 사용 |
| 1~2년 | 간단한 지시를 따르고 신체 부위나 물건을 가리킵니다. | 10~50개의 단어를 사용하고 "더 많은 주스"와 같은 두 단어 구를 결합합니다. |
| 2~3년 | 간단한 질문과 기본 개념(크고 작은)을 이해합니다. | 200~300단어로 확장, 3~4단어 문장 사용 시작 |
| 3~4년 | 스토리를 이해하고 "무엇"과 "어디"에 대한 질문에 답합니다. | 완전한 문장을 사용하고, 짧은 이야기를 들려주고, 많은 질문을 합니다. |
| 5~6년 | 반대말을 이해하고 여러 단계의 지시를 따릅니다. | 완전한 문장을 사용하고, 짧은 이야기를 들려주고, 많은 질문을 합니다. |
These language development milestones not only help educators and caregivers assess whether a child is developing typically, but also point to broader patterns across other domains of development. For example, delayed expressive language might indicate related social-emotional or adaptive skills challenges, such as frustration tolerance or peer interaction.

유아기 언어 발달을 지원하는 방법
유아
Support begins with verbal interaction. Talk to the baby often using simple, clear words. Respond to coos and babbles as if they were part of a conversation. Use songs, rhymes, and expressive facial cues. This builds receptive language and emotional bonds, vital to language development.
유아/2세
사물에 이름을 붙이고, 행동에 이름을 붙이고, 말로 선택을 할 수 있는 기회를 충분히 제공하세요. 간단한 글이 적힌 책을 활용하고 자주 쓰이는 표현을 반복하세요. 아이들이 가리키고, 이름을 부르고, 따라 하도록 격려하세요. 이러한 초기 표현 능력은 모든 발달 영역에서 뛰어난 성과를 낼 수 있는 토대를 마련해 줍니다.
유치원/유치원
이 단계의 아이들은 어휘력이 빠르게 확장되고 완전한 문장을 형성하기 시작합니다. 스토리텔링, 질의응답 시간, 그리고 노래에 참여시켜 보세요. 개방형 질문("다음에 무슨 일이 일어날 것 같아?")은 언어 발달 영역에서 고차원적인 사고를 자극하고 조기 문해력을 향상시킵니다.
학령기
문법, 문장 구조, 그리고 서술 능력을 다듬는 데 집중하세요. 소리 내어 읽기, 단편 소설 쓰기, 그리고 그룹 토론 참여를 장려하세요. 맥락에 맞춰 새로운 어휘를 소개하고, 아이들이 생각을 설명하거나 지시를 내리는 연습을 하도록 하세요. 이는 언어 발달과 인지 발달 모두에 매우 중요합니다.
사회정서적 발달 영역
Social-emotional development refers to how children understand emotions, form relationships, and manage their behavior in different settings. It is one of the most sensitive yet foundational developmental domains, influencing how children connect with others, build self-esteem, and participate in group learning environments.

사회정서적 발달의 핵심 요소
감정 인식 및 표현
아이들은 자신과 타인의 감정을 파악하는 법을 배웁니다. 행복, 슬픔, 분노와 같은 기본적인 감정을 인식하는 것부터 시작하여, 점차 당혹감이나 자부심과 같은 더 복잡한 감정의 이름을 붙이고 표현하는 능력을 발달시킵니다. 이러한 감정 어휘는 사회정서 발달 영역에서 매우 중요합니다.
자기 조절
This refers to a child’s ability to manage impulses, handle transitions, and cope with disappointment. This process includes strategies like deep breathing, asking for help, or using quiet spaces. Strong self-regulation supports participation in structured learning and connects with all developmental domains.
관계 구축
Children must learn to cooperate, share, take turns, and resolve conflicts. These skills grow through repeated social experiences, supported by responsive adults. Healthy peer interactions are one of the strongest indicators of progress in the social-emotional development domain.
공감과 관점 수용
아이들은 성장하면서 다른 사람들이 어떻게 생각하고 왜 그렇게 생각하는지 이해하기 시작합니다. 이러한 공감 능력은 친절, 팀워크, 도덕적 추론을 뒷받침하고, 우정과 공동체 참여를 더욱 깊게 하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
연령별 사회정서적 발달 이정표
Tracking social-emotional milestones helps educators and caregivers understand how children build relationships, express emotions, and develop behavioral control. These milestones are central to social-emotional development and are deeply interwoven with growth across other developmental domains.
| 연령대 | 일반적인 사회-정서적 이정표 |
|---|---|
| 0~12개월 | 기본적인 감정을 식별하고, 도움을 받아 차례를 지키며, 그룹 규칙을 이해하기 시작하고, 단어를 사용하여 갈등을 해결합니다. |
| 1~2년 | 친숙한 보호자를 선호하고, 얼굴 표정에 반응하며, 사회적 미소를 시작합니다. |
| 2~3년 | Expresses feelings verbally, shows early empathy, engages in 협동 플레이, may struggle with sharing |
| 3~4년 | 공감과 공정성을 보여주고, 감정을 보다 독립적으로 관리하며, 가까운 동료 관계를 형성합니다. |
| 5~6년 | Expresses feelings verbally, shows early empathy, engages in 협동 플레이, and may struggle with sharing |
While each child develops at their own pace, delays in these areas may signal broader challenges across the developmental domains, such as language difficulties (affecting emotion expression) or adaptive skill delays (affecting coping strategies). Early and consistent social-emotional support builds long-term resilience and school readiness.

유아기 사회정서적 발달을 지원하는 방법
유아
Emotional development starts with secure attachment. Respond to cries comfortably, maintain eye contact, and use a soothing tone. These early interactions build trust and form the emotional foundation of all developmental domains.
유아/2세
유아들이 자신의 감정을 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있도록 도와주세요. "장난감이 없어서 슬퍼." "부드러운 손길"이나 "차례를 기다려"와 같은 기본적인 사회적 규칙을 가르치기 시작하세요. 책과 인형을 활용하여 감정 표현과 사회적 상황을 연출해 보세요. 이러한 경험은 감정 표현과 조기 또래 인식을 발달시키는 데 도움이 됩니다.
유치원/유치원
Use group activities to teach cooperation, sharing, and friendship. Role-play situations to practice responses. Provide calm-down areas and visual aids to support self-regulation. Children need consistent adult guidance to navigate more complex emotional situations at this stage.
학령기
동료 간 토론과 성찰을 통해 문제 해결과 갈등 해결을 지원합니다. 일기 쓰기, 감정에 대한 열린 대화, 그리고 팀 활동 참여를 장려합니다. 이를 통해 사회정서 발달 영역에서 중요한 두 가지 기술인 공감 능력과 감성 지능이 더욱 향상됩니다.
적응형 개발 도메인
적응적 발달 영역은 아동이 일상생활에서 독립적으로 기능할 수 있도록 하는 실질적인 생활 기술을 의미합니다. 이는 가장 적용 가능한 발달 영역 중 하나이지만, 종종 간과되기는 하지만 아동의 교육 및 가정 환경 모두에서의 성공에 필수적입니다.

적응형 개발의 핵심 구성 요소
자기 관리 및 위생
Children gradually learn to brush their teeth, wash their hands, use the toilet, and care for their grooming needs. These self-care routines are crucial in the adaptive development and are often the earliest signs of independence.
옷 입기 및 수유
Using utensils, drinking from a cup, putting on shoes, and managing buttons or zippers are central adaptive milestones. These tasks develop gradually with practice and support and involve physical coordination and cognitive planning.
일상과 책임
아이들은 장난감 정리, 가방 싸기, 한 활동에서 다른 활동으로 전환하는 것과 같은 정해진 일상을 따르는 법을 배웁니다. 이를 통해 아이들은 책임감을 키우고 교실에서 기대하는 바에 적응하게 되는데, 이는 모든 발달 영역과 연결되는 기술입니다.
안전 및 사회적 규칙
Understanding and following safety instructions (like “don’t touch the stove” or “stay with the group”) also fall under adaptive behavior. As children grow, their ability to recognize danger and act accordingly reflects their maturity.
연령별 적응 발달 이정표
The adaptive development domain tracks how children develop independence through self-care, responsibility, and following routines. These skills evolve gradually and reflect how well a child is adapting to the expectations of daily life at home, in school, and in the community.
| 연령대 | 일반적인 적응적 이정표 |
|---|---|
| 0~12개월 | 손가락으로 먹이를 먹기 시작하고, 간단한 일상(예: 취침 시간)에 반응하고, 익숙한 물건을 선호합니다. |
| 1~2년 | Dresses with minimal help, uses the toilet independently, and puts away toys or materials. |
| 2~3년 | 간단한 일상 생활을 따르고, 도움을 받아 일부 옷을 벗고, 손을 씻고 말립니다. |
| 3~4년 | 숟가락으로 먹이려고 시도하고, 옷 입는 데 협조하고, 손 씻는 데 도움을 주고, 변기 훈련을 시작합니다. |
| 5~6년 | 최소한의 도움을 받아 옷을 입고, 화장실을 독립적으로 사용하고, 장난감이나 물건을 치웁니다. |
이러한 적응 발달 이정표는 다른 발달 영역과도 교차합니다. 예를 들어, 소근육 운동 능력의 지연은 아동의 옷 단추 끼우기 능력에 영향을 미칠 수 있으며, 인지 발달 지연은 아동의 단계별 일상 생활 이해에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 따라서 적응 발달은 단순히 "실용적인 생활 기술"만을 의미하는 것이 아니라, 자립과 학습에 대한 전반적인 준비 상태를 나타내는 핵심 지표입니다.

유아기 적응 발달을 지원하는 방법
유아
유아기부터 적응 행동의 기초가 형성됩니다. 수유, 수면, 기저귀 갈기에 대한 예측 가능한 루틴을 정해 주세요. 아기가 손가락이나 부드러운 숟가락으로 스스로 먹는 것을 탐구하도록 하세요. 일관성은 신뢰를 쌓고 모든 발달 영역에서 조기 발달을 지원합니다.
유아/2세
Encourage toddlers to try dressing themselves, wash their hands with assistance, and use utensils. Set simple routines (e.g., “first we eat, then we clean up”) and offer gentle guidance. Celebrate independence and allow plenty of time for children to attempt tasks themselves.
유치원/유치원
Children in this stage can handle many self-care tasks with minimal help. Provide visual schedules, labeled storage for belongings, and consistent routines. Reinforce responsibility through simple chores like setting the table or organizing supplies. These experiences strengthen the adaptive development domain alongside social and cognitive growth.
학령기
간단한 간식 준비, 가방 싸기, 여러 단계의 지시 따르기 등 더 복잡한 일을 맡기세요. 문제 해결 능력을 키우세요. "오늘 학교에 뭘 가져가야 할까?"처럼 아이들이 일상 생활에서 책임감을 갖고 스스로 해낼 수 있도록 하세요. 자신감과 독립심을 기르세요.

발달 지연과 그 원인
In early childhood education, developmental delays refer to a child not reaching expected milestones within one or more developmental domains. These delays can vary widely in severity, may be temporary or ongoing, and often affect a child’s ability to participate fully in daily activities, learning environments, or social interactions.
While some delays are immediately apparent, others emerge gradually. Recognizing them early and providing the proper support can significantly affect a child’s long-term development.

영역별 발달 지연 유형
발달의 다섯 가지 영역을 이해하면 전문가와 가족이 어떤 영역에 지원이 필요한지 파악하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 각 영역에 대한 지연의 일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다.
1. 신체 발달 지연
The physical development involves gross motor skills (like crawling, walking, running) and fine motor skills (such as grasping small objects or drawing). Delays in this domain often become noticeable during infancy or toddlerhood and can affect a child’s ability to explore, play, and develop independence.
일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다.
- 9개월까지 지지 없이 앉는 데 어려움
- 예상 연령대에 비해 기어다니거나 걷지 못함
- 작은 물건을 잡거나 도구를 사용하는 데 어려움이 있음
- 달리거나 올라갈 때 균형 감각이나 협응력이 부족함
2. 인지 발달 지연
인지 발달 영역은 아이의 사고력, 문제 해결 능력, 기억력, 그리고 세상을 이해하는 능력과 관련이 있습니다. 인지 발달 지연은 기본 개념 이해, 인과 관계 추론, 또는 호기심 부족으로 나타날 수 있습니다.
일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다.
- 원인과 결과를 이해하는 데 어려움
- 간단한 지시를 따르는 데 어려움이 있음
- 작업 탐색이나 해결에 대한 관심이 제한됨
- 기억력이나 주의력에 문제가 있음
3. 언어 발달 지연
언어 발달 영역은 두 가지 핵심 요소로 구성됩니다. 수용 언어(다른 사람의 말을 이해하는 능력)와 표현 언어(단어, 수화, 몸짓을 사용하여 의사소통하는 능력)입니다. 이 영역의 발달 지연은 유아기에 가장 흔하게 나타나며, 빠르면 12~18개월부터 관찰될 수 있습니다.
일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다.
- 12개월이 되어도 중얼거리거나 손가락질하지 마세요
- 2~3세까지 어휘가 제한되거나 간단한 문장을 형성할 수 없음
- 질문이나 지시 사항을 이해하는 데 어려움이 있음
- 욕구를 표현할 수 없어 좌절감
4. 사회 정서적 발달 지연
이 영역은 아이들이 관계를 형성하고, 감정을 조절하고, 사회적 신호를 이해하는 방식에 초점을 맞춥니다. 사회정서적 영역의 발달 지연은 교실 내 행동, 협동심, 그리고 정서적 회복력에 상당한 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다.
- 눈을 마주치지 않거나 다른 사람과 놀고 싶어하지 않음
- 잦은 강렬한 짜증이나 감정 폭발
- 다른 사람의 감정이나 사회적 신호를 이해하는 데 어려움
- 새로운 환경이나 이별 시 극심한 불안
5. 적응적 발달 지연
The adaptive development domain refers to practical life skills that help children function independently. These include self-care, daily routines, and understanding social rules. Delays here are often first noticed when a child cannot complete age-appropriate tasks without assistance.
일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다.
자기 관리나 개인적 책임에 대한 관심 부족
연령에 따른 기대치에 비해 독립적으로 옷 입기, 식사하기, 화장실 이용이 불가능함
일상이나 전환에 적응하기 어려움
기본적인 작업에 대한 성인의 과도한 의존
발달 지연의 일반적인 원인
지연은 다양한 요인으로 인해 발생할 수 있으며, 대개 두 가지 범주로 나뉩니다.
생물학적 원인
- 조산
- 유전적 질환(예: 다운 증후군)
- 신경학적 상태
- 출산 합병증이나 외상
- 만성 질환
환경적 원인
- 자극이나 상호작용이 부족함
- 일관성 없는 돌봄이나 방치
- 독소(예: 납) 노출
- 영양실조나 안전하지 못한 환경
- 가정 내 트라우마, 스트레스 또는 불안정
In many cases, developmental delays result from a combination of biological and environmental factors. Regardless of the root cause, early detection and timely intervention are key.
학습에 영감을 주는 공간을 디자인할 준비가 되셨나요? 교실의 필요에 맞춘 맞춤형 가구 솔루션을 위해 저희에게 문의하세요.
강력한 파트너십 구축: 발달 지연 아동 지원에 있어 교사와 가족의 역할
발달 지체 아동을 지원하는 것은 개인의 노력 그 이상을 요구합니다. 교육자, 가족, 그리고 지원 전문가들이 함께 책임을 져야 합니다. 학교는 체계적인 환경과 전문적인 서비스를 제공하는 반면, 가족은 자녀의 필요, 선호도, 그리고 일상 행동에 대한 깊이 있고 개인적인 이해를 제공합니다. 포용적인 유아 교육의 맥락에서 이러한 협력은 단순히 유익할 뿐만 아니라 필수적입니다.
파트너십을 위한 법적 및 전문적 프레임워크
미국을 포함한 많은 국가에서 장애인 교육법(IDEA) 장애 및 발달 지연이 있는 어린이가 다음을 받을 수 있도록 보장합니다. 무상 적정 공교육(FAPE) 에서 최소 제한 환경(LRE)이 법의 핵심은 부모와 교육자가 의사 결정에 있어 동등한 파트너라는 것입니다. 교사는 교육학적 전문 지식과 개입 기회를 제공하고, 부모는 모든 발달 영역에 걸쳐 지원 전략을 미세 조정할 수 있는 중요한 맥락과 일상적인 피드백을 제공합니다.
This partnership becomes particularly vital when consistent, in-person services are disrupted, such as during public health crises or school transitions. Flexibility, clear communication, and shared expectations help maintain support continuity regardless of the setting.
도전을 이해하고 부담을 공유하다
Even in ideal circumstances, parenting a child with developmental delays is a complex and demanding role. Families may manage multiple responsibilities, from physical therapy routines to behavior interventions and academic reinforcement. The expectation to simultaneously serve as a caregiver, teacher, speech therapist, and emotional anchor can be overwhelming.
On the other hand, teachers must balance many learners’ needs within often-limited resources. Without strong collaboration, misalignment can lead to missed opportunities for timely intervention or inconsistent strategies between home and school. The key to success lies in mutual understanding and role clarity.
효과적으로 협업하는 실용적인 방법
조기에 협력하면 효과적인 개입을 위한 토대가 마련됩니다. 발달 지연이 확인되면 조기 개입이라고 하는 시기적 지원을 통해 모든 발달 장애에 걸쳐 장기적 결과를 극적으로 개선할 수 있습니다.그러나 이 과정은 고립된 상태에서 이루어지지 않습니다. 가족, 교사, 그리고 전문가 간의 강력하고 조율된 파트너십이 필요합니다.
그러한 파트너십을 구축하기 위한 주요 전략은 다음과 같습니다.
- 열린 소통을 구축하세요: 일일 기록, 주간 점검, 커뮤니케이션 앱 등 일관된 방식으로 업데이트를 공유하세요. 가족들에게 관찰 가능한 행동, 새로운 진전, 또는 반복되는 어려움을 보고하도록 장려하세요. 이러한 피드백을 통해 교사는 학습 전략을 조정하거나 필요한 경우 공식 평가를 의뢰할 수 있습니다.
- 조기 개입 서비스 활성화: Educators and families should act quickly once concerns are noted. Depending on the child’s needs, early intervention may include speech therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, or developmental play sessions. Some children may also require special education support plans or ongoing developmental screenings. These services are most effective when coordinated between schools, healthcare providers, and families.
- 지원 계획 공동 작성: Teachers and parents should set clear, shared goals that align with the child’s needs across multiple domains of development. These may include milestones like “uses three-word phrases,” “puts on shoes independently,” or “follows two-step directions.” When everyone knows the goals and how to reinforce them, intervention becomes more effective and consistent across environments.
- 시각적 도구와 일상 루틴을 활용하세요: Visual schedules, first-then charts, and emotion thermometers help children anticipate transitions and regulate behavior. These methods are particularly effective for children who struggle with adaptive or social-emotional development.
- 환경 조정: Create calm, structured learning spaces at school and home. Educators can guide families in setting up sensory-friendly environments, using flexible seating, and providing fidget tools or quiet zones. These supports enhance focus and self-regulation skills that connect directly to multiple developmental domains.
- 진행 상황을 축하하고 그에 따라 조정하세요: Monitor each child’s response to interventions and adjust as needed. Small achievements—whether zipping a jacket, initiating a greeting, or completing a story—deserve recognition. Ongoing progress reviews help maintain momentum and keep support plans relevant.

In short, early intervention is not just about services—it’s about shared action. When families and educators collaborate with purpose and urgency, children with developmental delays receive the structured, personalized support they need to thrive across every development domain.
발달 영역 이정표 모니터링에서 정기 평가의 역할
Regular assessments help children develop appropriately across the five developmental domains: physical, cognitive, language, social-emotional, and adaptive. These assessments provide measurable insights into whether a child is meeting age-expected milestones or showing signs of delay.
정기 평가의 주요 이점:
- 조기 식별: 학습이나 행동에 영향을 미치기 전에 발달 지연을 감지합니다.
- 타겟 지원: Educators can tailor activities and interventions to the child’s needs.
- 진행 상황 추적: 개발의 모든 영역에서 시간에 따른 성장을 측정합니다.
- 협력적 이해: 교사의 관찰과 가족의 의견을 결합하여 완전한 발달 프로필을 작성합니다.
일반적인 평가 도구:
- Ages & Stages Questionnaire (ASQ): 운동, 언어, 문제 해결, 사회적 기술의 진행 상황을 추적합니다.
- 관찰 체크리스트: Teachers use these to monitor behavior and skill acquisition during daily routines.
- 아동 포트폴리오: 여러 도메인에 걸쳐 성장을 보여주는 업무 샘플과 문서를 수집합니다.
평가를 일상 활동에 포함시키고 결과를 지속적으로 검토함으로써 교육자는 발달상의 격차에 조기에 적절하게 대응할 수 있습니다.
어떤 발달 영역도 단독으로 존재할 수 없는 이유: 아이의 성장을 형성하는 숨겨진 연결 고리
Though each of the five developmental domains—physical, cognitive, language, social-emotional, and adaptive—represents a distinct aspect of child development, they are deeply interconnected in practice. Children grow as whole beings, not in isolated parts. Progress in one domain often supports others, while delays in a single area can have cascading effects.
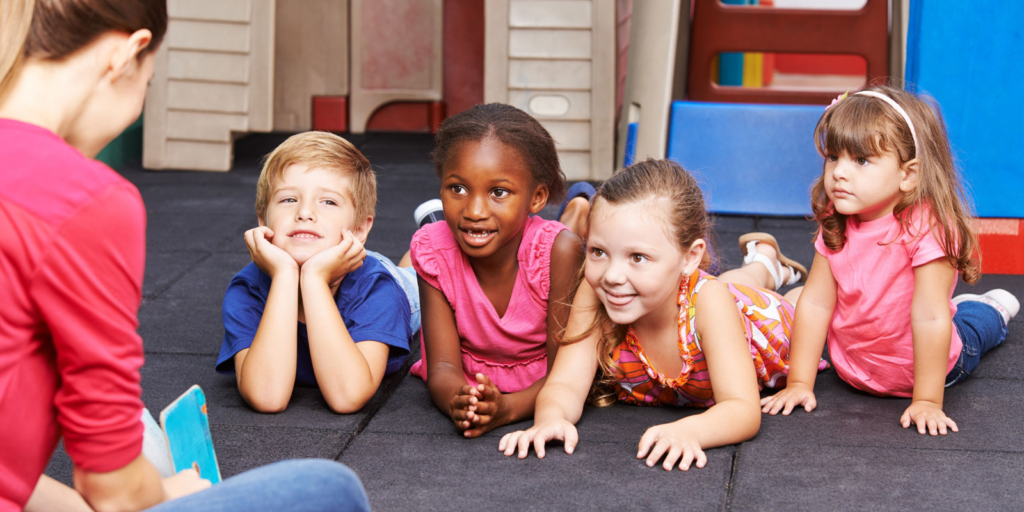

예를 들어:
- A child with underdeveloped fine motor skills (physical domain) may struggle with holding a pencil, directly impacting early writing and drawing tasks (cognitive domain).
- 어휘력이 부족하거나 말하는 능력이 늦은 경우(언어 영역) 어린이가 감정을 표현하는 데 어려움을 겪을 수 있으며, 때로는 좌절하거나 행동이 폭발하는 경우(사회-정서적 영역)가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 감정 조절에 어려움이 있는 경우(사회-정서적 영역) 어린이가 집단 일상에 적응하거나 옷 입기, 혼자 식사하기와 같은 자조 활동에 참여하는 능력(적응적 영역)에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
- 긍정적인 측면에서, 강력한 문제 해결 능력과 기억력(인지 영역)은 종종 더 빠른 언어 습득과 더 정교한 문장 구성(언어 영역)으로 이어진다.
교육자, 가족, 그리고 프로그램 설계자는 발달 영역 간의 이러한 역동적인 관계를 항상 고려해야 합니다. 균형 잡히고 반응적인 학습 환경은 모든 영역을 고립된 것이 아니라 조화롭게 지원하는 것을 목표로 해야 합니다.
개발에 대한 전체론적 접근 방식을 촉진하는 방법은 무엇인가?
발달에 대한 전체론적 접근은 아동을 단편적인 부분이 아닌 온전한 존재로 보는 것을 의미합니다. 하나의 발달 영역에만 고립적으로 집중하기보다는, 신체적, 인지적, 언어적, 사회정서적, 적응적 발달 영역 간의 상호 연관성을 강조하고, 동시에 의도적으로 이를 지원하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
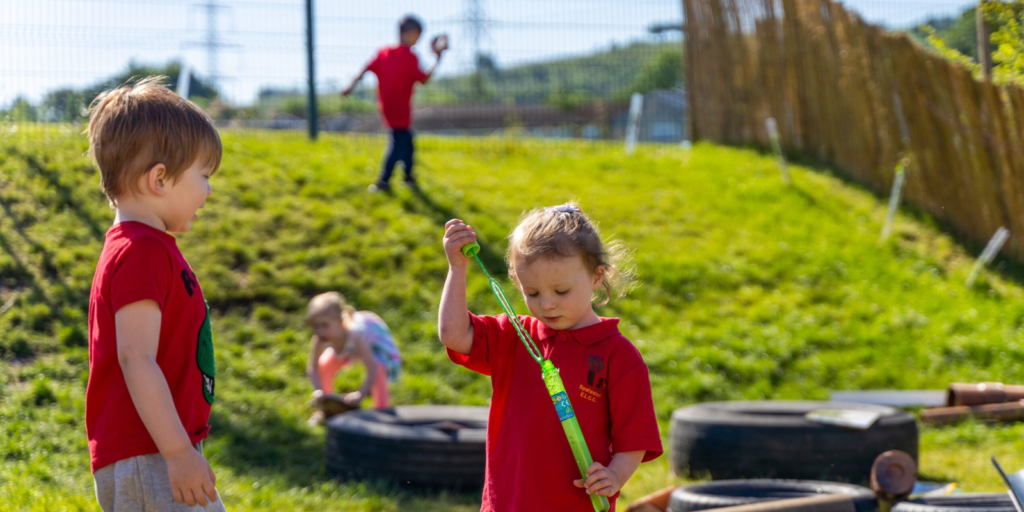

1. 통합 학습 경험 설계
활동은 여러 개발 영역을 동시에 다루어야 합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
- In one lesson, a storytelling activity that includes drawing, retelling, and group discussion builds language, cognitive, fine motor, and social-emotional skills.
- 교실에서 요리하는 것은 적응적 일상, 정밀 운동 조절, 순서(인지) 및 협동심을 발달시킵니다.
These integrated experiences reflect how real life develops—fluidly, not in isolated blocks.
2. 관계와 정서적 안전을 우선시하세요
교사와 아동 간의 돈독한 관계는 모든 영역에서 발달의 토대를 형성합니다. 정서적 안정감은 학습, 사회적 상호작용, 그리고 자조 활동에서 위험을 감수할 수 있도록 합니다. 아이들은 자신이 주목받고, 귀 기울여지고, 존중받는다고 느낄 때 가장 잘 배웁니다.
- 일관된 일상과 긍정적인 행동 지침을 활용하세요
- 아이들의 감정을 인정하고 이를 명명하도록 도와주세요
- 구조화된 놀이를 통해 동료 간 상호 작용을 촉진합니다.
이는 사회적 정서적 발달 영역을 강화하고, 이는 다시 다른 모든 영역을 뒷받침합니다.
3. 개인차 지원
전체론적 접근 방식은 모든 아동에게 동일하게 적용되지 않습니다. 각 아동은 고유한 발달 경로를 가지고 있습니다. 교육자는 모든 발달 영역에서 아동의 강점과 약점을 뒷받침할 수 있도록 학습 기회를 면밀히 관찰하고 조정해야 합니다.
- Provide differentiated materials and flexible goals.
- Use child portfolios to track growth in all areas.
- Work closely with families to build consistent support between home and school.
결론
신체, 인지, 언어, 사회정서, 적응의 다섯 가지 발달 영역을 이해하는 것은 단순히 아이의 성장을 추적하는 것이 아닙니다. 학습 환경, 교육 과정, 그리고 유아 발달을 이끄는 상호작용을 형성하는 정보에 기반한 의도적인 결정을 내리는 것입니다. 각 영역은 아이의 고유한 필요와 잠재력을 들여다볼 수 있는 창을 제공하며, 교육자, 가족, 그리고 시스템이 목적을 가지고 협력할 때 그 결과는 혁신적입니다.
고품질 유아 교육은 우연히 이루어지지 않습니다. 때로는 말 그대로 아동 발달 이론과 일치하는 틀 위에 세워집니다. 영역 기반 관찰 도구부터 학습 공간의 물리적 설정모든 선택은 중요합니다. 그렇기 때문에 장기적으로 성공하는 프로그램은 가구가 단순한 가구가 아니라 교육학의 연장선이라는 것을 이해하는 전문 파트너와 긴밀히 협력하는 경우가 많습니다. 다음과 같은 제조업체들이 있습니다. 웨스트 쇼어 가구이러한 발달적 요구를 염두에 두고 조기 학습 환경을 설계하는 자들은 교육자들이 가장 중요한 것을 실천하도록 돕는 데 있어 조용하지만 중요한 역할을 합니다. 모든 선반, 의자, 테이블이 아동 발달의 현실에 맞춰 만들어질 때, 아이들은 단순히 앉아 있는 것이 아니라 성장하기 때문입니다.
Ultimately, supporting children across all developmental domains requires vision, strategy, and deep respect for the complexity of early learning. The tools we use, the environments we build, and the relationships we cultivate all contribute to whether a child passes through a classroom or thrives in it.
자주 묻는 질문
1. 3가지 개발 영역과 5가지 개발 영역의 차이점은 무엇입니까?
The three domains—cognitive, affective, and psychomotor—are typically used in educational psychology to describe how people learn. The five domains of development—physical, mental, language, social-emotional, and adaptive—are used in early childhood development to describe how children grow.
2. 평생 학습과 기술 개발이 포함되는 핵심 영역은 무엇입니까?
인지 발달 영역은 평생 학습, 사고, 문제 해결, 시간이 지남에 따라 지식과 기술 습득과 가장 밀접하게 연관되어 있습니다.
3. 인지 능력과 지식 보유는 어떤 영역에 포함됩니까?
These are key cognitive development functions, which cover memory, reasoning, understanding, and mental processing.
4. '학습 접근 방식'은 발달 영역으로 간주됩니까?
호기심, 끈기, 문제 해결 태도와 같은 학습 접근 방식은 핵심 영역은 아니지만, 주로 인지적 영역과 사회 정서적 영역을 포함한 5가지 발달 영역 전체에 영향을 미치는 교차 영역 요인으로 취급되는 경우가 많습니다.
5. 정서적 영역은 인지적 영역과 어떻게 다릅니까?
정서적 영역은 감정, 태도, 사회적 행동을 포함하는 반면, 인지적 영역은 사고, 추론, 기억과 같은 지적 기능에 초점을 맞춥니다.
6. 신체 발달은 발달 영역에 어떻게 들어맞나요?
신체 발달은 대근육 운동 능력과 소근육 운동 능력을 아우르는 5대 핵심 발달 영역 중 하나입니다. 신체 발달은 아동의 탐구, 상호작용, 일상생활 참여 능력을 지원하여 독립심과 학습 준비의 기초를 형성합니다.
7. 사회적, 정서적 발달이 어린이에게 중요한 이유는 무엇입니까?
Social-emotional development helps children build relationships, understand emotions, and regulate behavior. It supports cooperation, empathy, and confidence—skills essential for classroom success and lifelong mental well-being.
8. 발달 영역은 모든 문화권에서 보편적입니까?
The five developmental domains are universal, but the timing, expression, and emphasis of development can vary by culture. For example, some cultures may prioritize group harmony (social-emotional) over verbal expression (language), shaping how milestones are viewed.
9. 유아교육에서 발달 영역은 어떻게 평가됩니까?
Educators assess developmental domains through observation, checklists, screenings, and family input. Tools such as ASQ (Ages & Stages Questionnaire) or standardized assessments help track milestones and identify any delays early.





